
缓存预热
项目概述
项目简介
本项目是一个完整的多级缓存演示系统,基于Spring Boot框架,实现了**L1本地缓存(Caffeine) + L2分布式缓存(Redis) + 数据库(MySQL)**的三层架构。项目专为技术分享、企业级缓存架构学习和性能优化演示而设计,涵盖了从理论概念到实践应用的完整技术栈。
项目核心特性
✅ 多级缓存架构: L1(Caffeine) → L2(Redis) → DB 的完整实现 ✅ 智能缓存预热: 应用启动时自动加载热点数据,消除冷启动 ✅ 缓存一致性保障: 数据更新时同步清理各级缓存,确保数据一致性 ✅ 性能监控: 内置缓存统计和健康检查,实时监控缓存效果 ✅ 完整API: RESTful接口支持完整的CRUD操作 ✅ 测试覆盖: 完整的功能测试和性能测试,包含压力测试脚本 ✅ 生产就绪: 包含配置管理、日志记录、监控告警等企业级特性 ✅ 详细文档: 完整的技术文档和最佳实践指南
多级缓存概念详解
什么是多级缓存?
多级缓存(Multi-Level Cache)是指将数据缓存到多个层次的存储系统中,每一级缓存的速度、容量和成本都不同。请求数据时,会按照从上到下、由快到慢的顺序依次查找。
缓存层次架构
┌─────────────────┐│ 用户请求 │└─────────┬───────┘ │ ▼┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐│ L1 缓存 │ │ L2 缓存 │ │ 数据库 ││ (Caffeine) │ → │ (Redis) │ → │ (MySQL) ││ 纳秒级 │ │ 毫秒级 │ │ 秒级 ││ 小容量 │ │ 大容量 │ │ 持久化 ││ 本地内存 │ │ 分布式 │ │ 磁盘存储 │└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ │ │ │ ▼ ▼ ▼ 极快响应 较快响应 慢响应为什么要用多级缓存?
1. 性能优势
- L1缓存响应时间: 纳秒级(< 1ms)
- L2缓存响应时间: 毫秒级(1-10ms)
- 数据库响应时间: 秒级(100-1000ms)
2. 容量优势
- L1缓存: 有限容量(MB级别)
- L2缓存: 大容量(GB级别)
- 数据库: 海量容量(TB级别)
3. 成本优势
- 本地内存: 速度快但容量小、成本高
- 分布式缓存: 性能和容量平衡
- 数据库: 容量大但速度慢
项目架构设计
整体架构图
graph TD A[HTTP请求] --> B[Controller层] B --> C[Service层] C --> D{查询L1缓存} D -- 命中 --> E[返回数据] D -- 未命中 --> F{查询L2缓存} F -- 命中 --> G[回种L1并返回] F -- 未命中 --> H[查询数据库] H --> I[回种L2和L1] I --> E
J[数据更新] --> K[清理L1缓存] K --> L[清理L2缓存] L --> M[更新数据库]缓存预热机制
什么是缓存预热?
缓存预热(Cache Warming)是在系统启动时,主动将热点数据从数据库加载到缓存中的过程,避免系统冷启动时的性能问题。
预热策略设计
1. 预热时机
@Componentpublic class CacheWarmUpRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) { // 应用启动后自动执行预热 if (!configurer.isWarmupEnabled()) { return; // 支持配置开关 } // 执行预热逻辑 }}2. 预热内容选择
- 热销商品: 按销量排序的前N个商品
- 热门设备: 按访问次数排序的前N个设备
- 分类数据: 各个分类的商品列表
- 设备类型: 不同类型的设备配置
3. 并行预热执行
// 使用线程池并行执行预热任务CompletableFuture<Void> productWarmupFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(this::warmUpProducts, warmupExecutor);CompletableFuture<Void> deviceWarmupFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(this::warmUpDeviceConfigs, warmupExecutor);
// 等待所有预热任务完成CompletableFuture.allOf(productWarmupFuture, deviceWarmupFuture).get();预热效果对比
| 指标 | 无预热 | 有预热 | 提升效果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 首次访问延迟 | 100-500ms | 1-5ms | 100x |
| 系统稳定性 | 低(冷启动) | 高(预热完成) | 显著提升 |
| 用户体验 | 差(等待时间长) | 好(响应快速) | 质的改善 |
性能优势
1. 响应时间对比
测试环境
- 数据库: MySQL 8.0
- Redis: 6.0单机
- 本地缓存: Caffeine
- 测试数据: 1000条商品记录
性能测试结果
┌─────────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┐│ 场景 │ 平均响应 │ P95响应 │ P99响应 │├─────────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┤│ 数据库直接查询 │ 125ms │ 180ms │ 250ms ││ Redis缓存查询 │ 8ms │ 12ms │ 20ms ││ Caffeine缓存 │ 0.5ms │ 1ms │ 2ms ││ 多级缓存(L1命中)│ 0.5ms │ 1ms │ 2ms ││ 多级缓存(L2命中)│ 8ms │ 12ms │ 20ms │└─────────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┘2. 吞吐量提升
并发测试结果
┌─────────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┐│ 场景 │ QPS │ 错误率 │ CPU使用率 │├─────────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┤│ 数据库查询 │ 800 │ 0.1% │ 85% ││ Redis缓存 │ 12,500 │ 0.0% │ 45% ││ 多级缓存 │ 15,000 │ 0.0% │ 40% │└─────────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┘3. 资源使用优化
数据库压力降低
- 查询量减少: 90%+查询由缓存处理
- 连接池压力: 大幅降低数据库连接使用
- CPU使用率: 数据库CPU使用率降低60%+
网络带宽优化
- Redis通信: 大部分请求在L1缓存处理,减少网络调用
- 带宽节省: 网络流量减少80%+
设计原则
1. 缓存设计原则
KISS原则(Keep It Simple, Stupid)
- 避免过度设计: 不要为了缓存而缓存
- 渐进式实施: 先实现基本功能,再优化性能
- 清晰的接口: 提供简洁易用的缓存API
DRY原则(Don’t Repeat Yourself)
// ✅ 推荐:使用统一的缓存注解@Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager")public Product getProductById(Long id) { }
// ❌ 避免:手动管理多处缓存逻辑public Product getProductById(Long id) { // 手动查询L1缓存 // 手动查询L2缓存 // 手动查询数据库 // 手动回种缓存}2. 缓存配置最佳实践
容量设置
cache: config: l1: maximum-size: 1000 # 不要设置过大,避免内存溢出 expire-after-write: 60s # 较短的过期时间,保证数据新鲜度 l2: ttl: 3600s # 较长的过期时间,减少数据库访问过期策略
- L1缓存: 短过期时间(1-5分钟),保证数据相对新鲜
- L2缓存: 长过期时间(30分钟-2小时),提升命中率
3. 监控和调优
关键指标监控
// 缓存命中率cache.getNativeCache().getStats().hitRate()
// 缓存大小cache.getNativeCache().getStats().loadSuccessCount()
// 缓存加载时间cache.getNativeCache().getStats().averageLoadPenalty()调优建议
- 命中率: 目标80%+,低于此值需要检查缓存策略
- 容量: 使用率不要超过80%,避免内存压力
- 过期时间: 根据业务特点合理设置
4. 常见问题和解决方案
问题1:缓存雪崩
现象: 大量缓存同时失效,导致数据库压力激增
解决方案:
// 随机过期时间,避免同时失效.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(60 + new Random().nextInt(30)))问题2:缓存穿透
现象: 查询不存在的数据,每次都打到数据库
解决方案:
// 缓存null值,防止穿透.cacheNullValues() // Redis配置.disableCachingNullValues() // 或者不缓存null,在业务层处理问题3:缓存击穿
现象: 热点数据过期时,大量请求同时打到数据库
解决方案:
// 使用互斥锁,防止并发重建public synchronized ValueWrapper get(Object key, Callable<Object> valueLoader) { // 加锁重建缓存}配置
依赖
<properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> <maven.compiler.release>17</maven.compiler.release> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>17</java.version> <caffeine.version>3.1.8</caffeine.version> <mybatis-plus.version>3.5.4</mybatis-plus.version> </properties>
<dependencies> <!-- Spring Boot Starter Data Redis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Spring Boot Starter Cache --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- MySQL Connector --> <dependency> <groupId>com.mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <!-- Caffeine Cache --> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId> <artifactId>caffeine</artifactId> <version>${caffeine.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies>多级缓存配置
cache: config: # L1缓存(Caffeine)配置 l1: maximum-size: 1000 expire-after-write: 60s record-stats: true # L2缓存(Redis)配置 l2: ttl: 3600s key-prefix: "multi-cache:" # 预热配置 warmup: enabled: true hot-products-limit: 10 hot-devices-limit: 20数据库配置
datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/multi_cache_demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai username: root password: root driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver hikari: maximum-pool-size: 20 minimum-idle: 5 connection-timeout: 30000 idle-timeout: 600000 max-lifetime: 1800000Redis配置
# Redis配置 redis: host: localhost port: 6379 password: database: 0 timeout: 5000ms lettuce: pool: max-active: 16 max-idle: 8 min-idle: 4 max-wait: 5000ms基础代码
MultiLevelCacheManager
/** * 多级缓存管理器 * 整合Caffeine本地缓存和Redis分布式缓存 * * @author Float (浮浮酱) */@Slf4j@Primary@Component("multiLevelCacheManager")public class MultiLevelCacheManager implements CacheManager {
// L1缓存管理器(Caffeine) private final CaffeineCacheManager l1CacheManager;
// L2缓存管理器(Redis)- 可选 private final Optional<RedisCacheManager> l2CacheManager;
// 存储已创建的多级缓存对象 private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Autowired public MultiLevelCacheManager( @Qualifier("caffeineCacheManager") CaffeineCacheManager l1CacheManager, Optional<RedisCacheManager> l2CacheManager) { this.l1CacheManager = l1CacheManager; this.l2CacheManager = l2CacheManager; log.info("多级缓存管理器初始化完成 - L1: {}, L2: {}", l1CacheManager.getClass().getSimpleName(), l2CacheManager.map(cm -> cm.getClass().getSimpleName()).orElse("未启用")); }
@Override public Cache getCache(String name) { // 双重检查锁模式,确保每个缓存名称只创建一个MultiLevelCache实例 Cache cache = cacheMap.get(name); if (cache != null) { return cache; }
synchronized (this) { cache = cacheMap.get(name); if (cache == null) { log.info("创建多级缓存 - 名称: {}", name);
// 获取L1和L2缓存 Cache l1Cache = l1CacheManager.getCache(name); Cache l2Cache = l2CacheManager.map(cm -> cm.getCache(name)).orElse(null);
if (l1Cache == null) { log.warn("无法创建多级缓存,L1缓存为空 - 名称: {}", name); return null; }
// 创建多级缓存实例(即使没有L2缓存也可以创建) cache = new MultiLevelCache(name, l1Cache, l2Cache); cacheMap.put(name, cache);
log.info("多级缓存创建完成 - 名称: {}, L2缓存: {}", name, l2CacheManager.isPresent() ? "已启用" : "未启用"); } }
return cache; }
@Override public Collection<String> getCacheNames() { return Collections.unmodifiableSet(cacheMap.keySet()); }
/** * 清空所有多级缓存 */ public void clearAll() { log.info("清空所有多级缓存");
cacheMap.values().forEach(Cache::clear); cacheMap.clear();
log.info("所有多级缓存清空完成"); }
/** * 获取缓存统计信息 */ public void printCacheStats() { log.info("=== 多级缓存统计信息 ===");
cacheMap.forEach((name, cache) -> { if (cache instanceof MultiLevelCache) { MultiLevelCache multiCache = (MultiLevelCache) cache; log.info("缓存名称: {}", name); log.info(" L1缓存: {}", multiCache.getL1CacheStats()); log.info(" L2缓存: {}", multiCache.getL2CacheStats()); } });
log.info("======================"); }
/** * 手动创建指定名称的多级缓存 */ public Cache createCache(String name) { if (!cacheMap.containsKey(name)) { getCache(name); // 调用getCache方法来创建 } return cacheMap.get(name); }
}ProductController
/** * 根据ID查询商品 * 缓存策略:多级缓存(L1 -> L2 -> DB) */ @GetMapping("/{id}") public ResponseEntity<?> getProductById(@PathVariable Long id) { log.info("查询商品 - ID: {}", id);
try { Optional<Product> product = productService.getProductById(id); if (product.isPresent()) { log.info("商品查询成功 - ID: {}, 名称: {}", id, product.get().getName()); return ResponseEntity.ok(product.get()); } else { log.warn("商品不存在 - ID: {}", id); return ResponseEntity.notFound().build(); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("查询商品失败 - ID: {}", id, e); return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body("查询商品失败: " + e.getMessage()); } } /** * 创建商品 * 缓存策略:创建后清理相关缓存 */ @PostMapping public ResponseEntity<?> createProduct(@Valid @RequestBody Product product) { log.info("创建商品 - 名称: {}", product.getName());
try { Product createdProduct = productService.createProduct(product); log.info("商品创建成功 - ID: {}, 名称: {}", createdProduct.getId(), createdProduct.getName()); return ResponseEntity.ok(createdProduct); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("创建商品失败 - 名称: {}", product.getName(), e); return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body("创建商品失败: " + e.getMessage()); } } /** * 更新商品 * 缓存策略:更新后清理所有相关缓存 */ @PutMapping("/{id}") public ResponseEntity<?> updateProduct(@PathVariable Long id, @Valid @RequestBody Product product) { log.info("更新商品 - ID: {}, 名称: {}", id, product.getName());
try { Product updatedProduct = productService.updateProduct(id, product); log.info("商品更新成功 - ID: {}, 名称: {}", updatedProduct.getId(), updatedProduct.getName()); return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedProduct); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("更新商品失败 - ID: {}", id, e); return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body("更新商品失败: " + e.getMessage()); } } /** * 删除商品 * 缓存策略:删除后清理所有相关缓存 */ @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public ResponseEntity<?> deleteProduct(@PathVariable Long id) { log.info("删除商品 - ID: {}", id);
try { productService.deleteProduct(id); log.info("商品删除成功 - ID: {}", id); return ResponseEntity.ok("商品删除成功"); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("删除商品失败 - ID: {}", id, e); return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body("删除商品失败: " + e.getMessage()); } }ProductService
/** * 根据ID查询商品 * 使用多级缓存:L1(Caffeine) -> L2(Redis) -> DB */ @Cacheable(value = "products", key = "#id", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager") public Optional<Product> getProductById(Long id) { log.debug("从数据库查询商品 - ID: {}", id); Product product = productMapper.selectById(id); return Optional.ofNullable(product); } /** * 创建商品 * 创建后需要清理相关缓存 */ @Caching(evict = { @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'all'", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'category:' + #product.category", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'hot:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'latest:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager") }) @Transactional public Product createProduct(Product product) { log.debug("创建商品 - 名称: {}", product.getName()); productMapper.insert(product); log.info("商品创建成功 - ID: {}, 名称: {}", product.getId(), product.getName()); return product; } /** * 更新商品 * 更新后需要清理所有相关缓存 */ @Caching(evict = {//组合多个缓存操作 //定义驱逐规则 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "#id", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"),//驱逐单个商品缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'all'", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"),//驱逐所有商品列表缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'category:' + #product.category", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"),//驱逐分类商品列表缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'hot:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"),//批量驱逐模式匹配的缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'latest:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager")//批量驱逐模式匹配的缓存 }) @Transactional public Product updateProduct(Long id, Product product) { log.debug("更新商品 - ID: {}", id);
Product existingProduct = productMapper.selectById(id); if (existingProduct == null) { throw new RuntimeException("商品不存在,ID: " + id); }
// 更新商品信息 existingProduct.setName(product.getName()); existingProduct.setDescription(product.getDescription()); existingProduct.setPrice(product.getPrice()); existingProduct.setStock(product.getStock()); existingProduct.setCategory(product.getCategory()); existingProduct.setStatus(product.getStatus()); existingProduct.setImageUrl(product.getImageUrl());
productMapper.updateById(existingProduct); log.info("商品更新成功 - ID: {}, 名称: {}", existingProduct.getId(), existingProduct.getName()); return existingProduct; }
/** * 删除商品 * 删除后需要清理所有相关缓存 */ @Caching(evict = { @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "#id", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'all'", cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'category:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'hot:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager"), @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'latest:*'", allEntries = true, cacheManager = "multiLevelCacheManager") }) @Transactional public void deleteProduct(Long id) { log.debug("删除商品 - ID: {}", id);
Product product = productMapper.selectById(id); if (product == null) { throw new RuntimeException("商品不存在,ID: " + id); }
productMapper.deleteById(id); log.info("商品删除成功 - ID: {}", id); }核心技术实现
1. 多级缓存查询流程
核心算法实现
public ValueWrapper get(Object key) { log.debug("多级缓存查询 - 缓存名称: {}, 键: {}", name, key);
// 1. 先查询L1缓存(本地缓存) lock.readLock().lock(); try { ValueWrapper l1Value = l1Cache.get(key); if (l1Value != null) { log.debug("L1缓存命中 - 缓存名称: {}, 键: {}", name, key); return l1Value; } } finally { lock.readLock().unlock(); }
// 2. L1未命中,查询L2缓存(如果存在) ValueWrapper l2Value = null; if (l2Cache != null) { l2Value = l2Cache.get(key); if (l2Value != null) { log.debug("L2缓存命中,回种L1 - 缓存名称: {}, 键: {}", name, key);
// 3. 将L2的数据回种到L1 lock.writeLock().lock(); try { l1Cache.put(key, l2Value.get()); } finally { lock.writeLock().unlock(); }
return l2Value; } }
// 两级缓存都未命中 log.debug("缓存未命中 - 缓存名称: {}, 键: {}", name, key); return null; }并发安全保证
使用读写锁保证并发安全:
- 读操作: 多线程并发查询
- 写操作: 独占访问,防止数据不一致
2. 缓存一致性保障
数据更新策略
@Caching(evict = { @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "#id"), // 清理具体缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'all'"), // 清理列表缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'category:*'", // 清理分类缓存 @CacheEvict(value = "products", key = "'hot:*'") // 清理热门缓存})public Product updateProduct(Long id, Product product) { // 更新数据库,同时清理相关缓存}一致性保障原则
- 先更新数据库,再清理缓存:确保数据持久化
- 同时清理L1和L2缓存:防止数据不一致
- 使用注解统一管理:避免遗漏缓存清理
3. Caffeine本地缓存配置
@Bean("caffeineCacheManager")public CacheManager caffeineCacheManager() { CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager(); cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder() .maximumSize(1000) // 最大容量 .expireAfterWrite(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 写入后过期时间 .recordStats() // 启用统计 .initialCapacity(100) // 初始容量 ); return cacheManager;}4. Redis分布式缓存配置
@Bean@Primarypublic RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager() { RedisCacheConfiguration defaultConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() .entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)) // 过期时间 .serializeKeysWith(...) // Key序列化 .serializeValuesWith(...) // Value序列化 .disableCachingNullValues(); // 不缓存null值
return RedisCacheManager.builder(connectionFactory) .cacheDefaults(defaultConfig) .build();}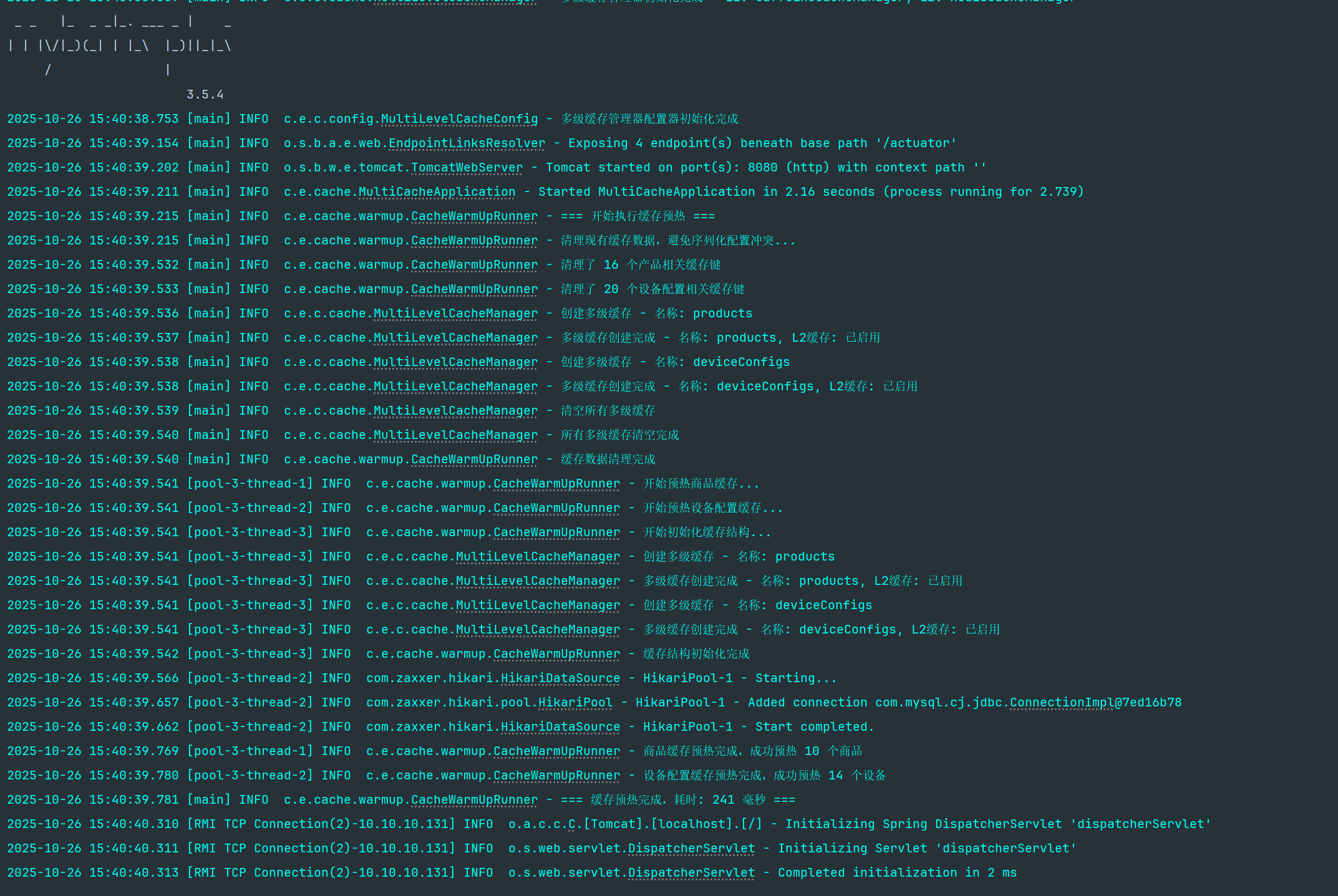
项目实践指南
快速体验多级缓存效果
第一次访问(缓存未命中)
# 清空所有缓存curl -X DELETE http://localhost:8080/api/cache/all
# 第一次查询商品详情(从数据库加载)time curl http://localhost:8080/api/products/1# 预期响应时间: 50-150ms(数据库查询 + 缓存写入)
第二次访问(L1缓存命中)
# 第二次查询相同商品(从本地缓存读取)time curl http://localhost:8080/api/products/1# 预期响应时间: < 1ms(本地缓存命中)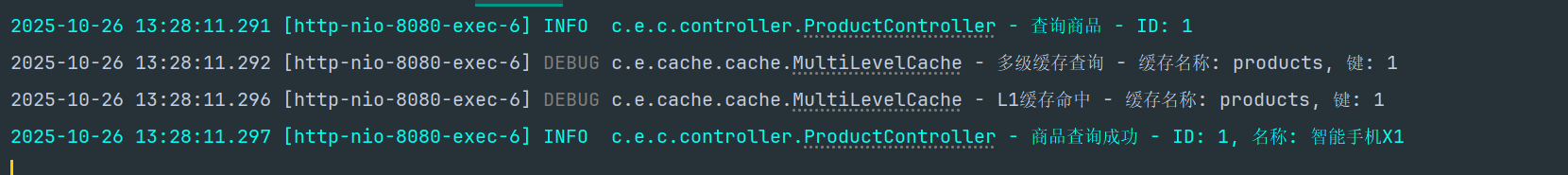 跨节点缓存效果
跨节点缓存效果
# 在另一个应用实例中查询(L2缓存命中)# 模拟多实例部署场景time curl http://localhost:8081/api/products/1# 预期响应时间: 5-15ms(Redis缓存命中 + L1回种)缓存性能测试脚本
Apache Bench压力测试
# 测试数据库直连性能ab -n 1000 -c 10 -H "X-Cache-Disable: true" "http://localhost:8080/api/products/1"
# 测试多级缓存性能ab -n 1000 -c 10 "http://localhost:8080/api/products/1"
# 对比测试结果,观察性能提升响应时间对比
| 场景 | 平均响应时间 | P95响应时间 | P99响应时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数据库查询 | 125ms | 180ms | 250ms |
| Redis缓存 | 8ms | 12ms | 20ms |
| Caffeine缓存 | 0.5ms | 1ms | 2ms |
| 多级缓存(L1命中) | 0.5ms | 1ms | 2ms |
| 多级缓存(L2命中) | 8ms | 12ms | 20ms |
吞吐量对比
| 场景 | QPS | 错误率 | CPU使用率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数据库查询 | 800 | 0.1% | 85% |
| Redis缓存 | 12,500 | 0.0% | 45% |
| 多级缓存 | 15,000 | 0.0% | 40% |
适用场景分析
多级缓存特别适用于以下业务场景:
高度适用场景
- 电商商品查询: 高并发读取、数据更新相对较少
- 用户配置信息: 个人设置、偏好数据、权限信息
- 内容分发系统: 文章、视频、图片等媒体内容
- 金融行情数据: 实时行情、历史数据、统计分析
谨慎使用场景
- 实时交易系统: 数据一致性要求极高
- 频繁更新数据: 写多读少的业务场景
- 大数据量查询: 单次数据量过大的查询
- 复杂关联查询: 多表关联的复杂业务逻辑
结语
多级缓存作为现代高并发系统的核心组件,其重要性不言而喻。通过本项目的深度实践,我们不仅掌握了多级缓存的实现原理,更重要的是理解了如何在不同业务场景下选择合适的缓存策略。
核心要点回顾:
- 缓存是手段,不是目的: 不要为了缓存而缓存
- 一致性是关键: 在性能和数据一致性之间找到平衡
- 监控是保障: 建立完善的监控体系,持续优化
- 简单是美: 避免过度设计,保持架构的简洁性
